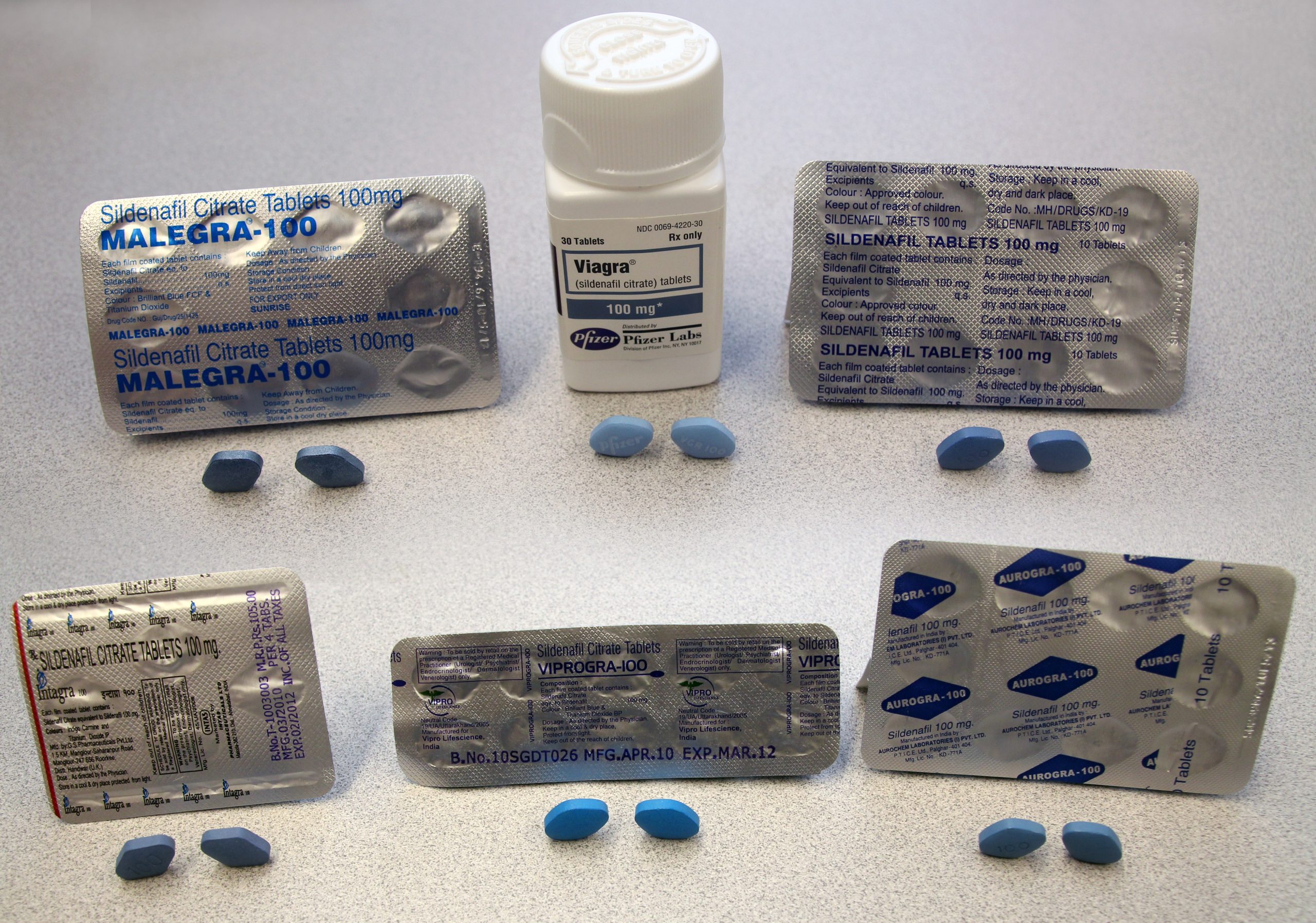
Need reliable information on Viagra? Start by understanding its primary function: improving erectile function by increasing blood flow to the penis. This effect stems from its active ingredient, sildenafil citrate, which inhibits an enzyme responsible for blood vessel constriction.
Viagra is a prescription medication, so consult your doctor before use. They can assess your overall health, identify potential drug interactions (like nitrates), and determine the appropriate dosage for your needs. Ignoring this step can lead to adverse effects. Common side effects include headaches, flushing, and nasal congestion, although these usually resolve quickly. Serious side effects are rare but require immediate medical attention.
Remember, Viagra isn’t a cure for erectile dysfunction; it’s a treatment to help achieve and maintain erections. Lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and stress management significantly impact sexual health. Your physician can provide tailored advice on these areas to complement Viagra’s effects. Open communication with your doctor is paramount for successful treatment and managing potential issues.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
- Pharmaceutical Products: Viagra
- Understanding Viagra’s Mechanism of Action
- Viagra: Dosage, Administration, and Potential Side Effects
- Viagra Alternatives and Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction
- Viagra: Safety Precautions and Contraindications
- Heart Conditions and Blood Pressure
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Vision Problems
- Liver and Kidney Disease
- Other Contraindications
- Summary of Precautions
Pharmaceutical Products: Viagra
Viagra, or sildenafil citrate, treats erectile dysfunction (ED) by increasing blood flow to the penis. It works by inhibiting an enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5), allowing for improved blood vessel dilation and stronger erections.
Consult your doctor before use. Viagra interacts with certain medications, including nitrates. Individuals with heart conditions or high blood pressure should discuss its use with their physician.
Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. Severe side effects are rare but include sudden vision loss or hearing loss. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience these.
Viagra is available in different dosages (25mg, 50mg, 100mg). Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose based on your individual needs and medical history. Dosage should not exceed 100mg in a 24-hour period.
Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully for proper use and storage. Store Viagra in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture.
Always purchase Viagra from reputable pharmacies to ensure authenticity and safety. Counterfeit medications can be dangerous and ineffective.
Remember, Viagra is a prescription medication. Self-treating ED can have serious consequences. Regular check-ups with your doctor are paramount for maintaining your health.
Understanding Viagra’s Mechanism of Action
Viagra, or sildenafil, works by inhibiting a specific enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). PDE5 breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a crucial molecule involved in the process of penile erection.
By blocking PDE5, Viagra allows cGMP levels to remain elevated. Increased cGMP relaxes the smooth muscles in the blood vessels of the penis, leading to increased blood flow.
This heightened blood flow is what creates and maintains an erection in response to sexual stimulation. It’s important to note that Viagra does not directly cause erections; it facilitates them by enhancing the body’s natural response to sexual stimulation.
The effects usually begin within 30-60 minutes of ingestion and can last for up to four hours. The specific duration and intensity of effects vary between individuals.
Individual responses to Viagra depend on factors like dosage, overall health, and the presence of other medications. Always consult a doctor before use to ensure safety and efficacy.
Viagra: Dosage, Administration, and Potential Side Effects
Consult your doctor to determine the appropriate dosage for you. Typically, the recommended starting dose is 50 mg taken orally, about one hour before sexual activity. This dosage can be adjusted based on individual response and effectiveness, ranging from 25 mg to 100 mg.
Viagra should be taken only as needed, not more than once daily. Do not take more than the prescribed dose.
Common side effects include:
- Headache
- Facial flushing
- Nasal congestion
- Indigestion
- Visual disturbances (blurred vision, sensitivity to light)
Less common, but potentially serious side effects require immediate medical attention:
- Prolonged erection (priapism)
- Sudden vision loss
- Sudden hearing loss
- Chest pain
- Irregular heartbeat
Certain medications and health conditions can interact with Viagra. Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, and any pre-existing medical conditions, particularly heart problems.
Factors like age, overall health, and other medications can influence how your body processes Viagra. Your doctor will help you determine the safest and most effective dose.
This information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new medication.
Viagra Alternatives and Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction
Consider Cialis or Levitra, both effective PDE5 inhibitors like Viagra, but with different durations of action. Cialis offers a longer-lasting effect, while Levitra may work faster for some men. Your doctor can help determine the best option for you.
If PDE5 inhibitors aren’t suitable, explore alternative treatments. These include injections directly into the penis (intracavernosal injections), vacuum erection devices, or penile implants. Each method provides a different approach to achieving an erection.
Lifestyle changes significantly impact erectile function. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques like meditation or yoga can improve overall health and sexual performance. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are also crucial.
Underlying medical conditions often contribute to ED. Conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure require medical attention, and treating these can positively affect erectile function. Discuss your medical history thoroughly with your doctor.
Hormone therapy may be an option if low testosterone levels are identified. Your physician can conduct blood tests to determine testosterone levels and suggest appropriate treatment if needed. This isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution, so personalized assessment is vital.
Counseling can address psychological factors contributing to ED, such as anxiety or performance pressure. A therapist can provide strategies to manage these issues and improve sexual confidence. This approach may be particularly helpful in conjunction with other treatments.
Remember: Consult your doctor before starting any new treatment for erectile dysfunction. They can assess your individual needs and recommend the most appropriate approach based on your medical history and lifestyle.
Viagra: Safety Precautions and Contraindications
Always consult your doctor before using Viagra, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions. This is paramount for your safety.
Heart Conditions and Blood Pressure
Viagra can lower blood pressure, potentially causing dizziness or fainting. Avoid Viagra if you have severe heart problems, uncontrolled high blood pressure, or recently experienced a heart attack or stroke. Discuss your cardiovascular health with your physician before considering Viagra.
Interactions with Other Medications
Certain medications can interact dangerously with Viagra. Nitrates, used to treat chest pain (angina), are particularly risky. Combining them with Viagra can cause a significant drop in blood pressure, leading to serious complications. Inform your doctor about all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Vision Problems
Rarely, Viagra can cause vision problems, such as blue-tinted vision or temporary blindness. If you experience these side effects, stop taking Viagra and seek immediate medical attention.
Liver and Kidney Disease
Individuals with severe liver or kidney disease should exercise caution and consult their doctor before using Viagra. Dosage adjustments might be necessary.
Other Contraindications
Viagra is not suitable for everyone. It’s contraindicated for men with certain blood disorders, anatomical deformities of the penis, or a history of priapism (prolonged erection).
Summary of Precautions
| Condition | Precautions |
|---|---|
| Heart disease | Consult your cardiologist; avoid if you have severe heart problems. |
| High blood pressure | Consult your doctor; avoid if uncontrolled. |
| Nitrate use | Strictly avoid concurrent use. |
| Liver or kidney disease | Consult your doctor; dosage adjustment may be needed. |
| Vision problems | Seek immediate medical attention if experienced. |
This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting any new medication.